What Are The Symptoms And Treatment Of Papillary Edema?
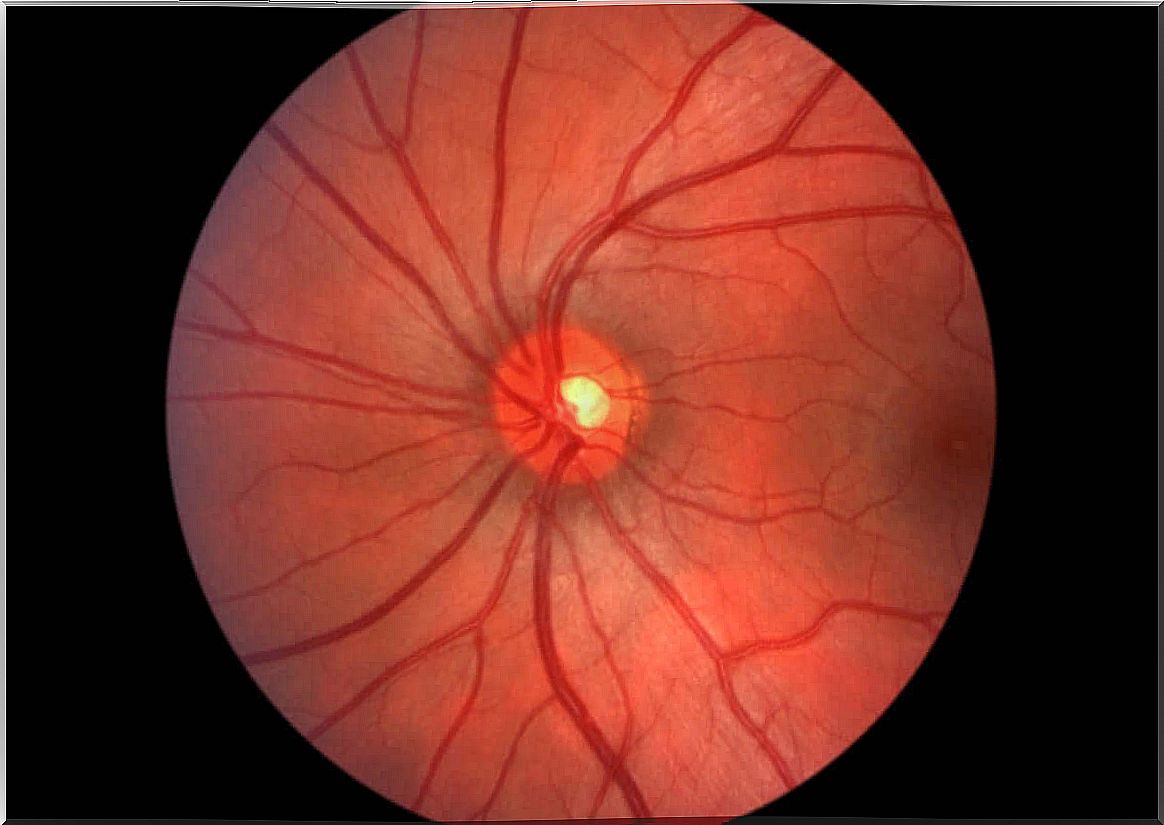
Papillary edema is a pathology that occurs in the eye. It consists of an inflammation in the area of the optic nerve closest to the retina, due to increased intracranial pressure.
In some cases, this pathology is asymptomatic, while in others it affects vision. The problem is that serious health problems, such as brain tumors, can hide behind this disease. Therefore, we explain everything you need to know in this article.
What is papillary edema?
Papillary edema consists, as we have already mentioned, of inflammation of the optic papilla of the eye. This usually occurs in both eyes at the same time, in the form of bilateral edema around the optic nerve papilla.
This pathology originates in intracranial hypertension. The skull is a fixed bone structure, where we find various organs and substances. One of them is the cerebrospinal fluid. When something inside this bone box increases in volume, it creates a pressure increase.
Papillary edema occurs when the intracranial pressure rises with over 200 mm of water. This increase may be due to a mass or tumor. Or on the other hand, it may be the result of an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid.
Possible causes
As we have just pointed out, the cause of papilla edema is cranial hypertension. This increases due to the amount of cerebrospinal fluid or the presence of abnormal masses in the brain.
These two situations are frequent in different scenarios. When we talk about abnormal masses, we are referring to tumors, abscesses from infection or blood due to bleeding.
However, according to a study published in the Journal of Neurology Supplements , the most common cause of papillary edema is idiopathic intracranial hypertension. This means that the pressure increases, but the underlying cause is unknown.
In other cases, it may be due to meningitis or encephalitis. An article in Acta Neurológica Colombiana confirms that it may also be a symptom of Wernicke’s syndrome. Other less common origins are the following:
- Guillain-Barré syndrome
- Hypervitaminosis A
- Tumors in the spinal cord
- Vena cava superior syndrome
What are the symptoms of papillary edema?
The symptoms of papillary edema vary. In the beginning, it is often asymptomatic, and specialists detect it only while performing a fundus examination. However, damage to the optic nerve begins to produce clear signs as it progresses.
In this sense, papillary edema ends up affecting a person’s vision. Your vision may become blurred, double, or even disappear for a few seconds. Many patients also experience sensitivity to light contrast.
Most episodes of vision loss last only a few seconds. In addition, intracranial hypertension also causes symptoms in itself. For example, it often involves headaches, nausea and vomiting.
The headache is stronger when you wake up in the morning and tends to get better during the day. In cases where meningitis is the cause, neck stiffness can develop in the neck.
The treatment of papillary edema
The main goal of treating papillary edema is to eliminate the cause of intracranial hypertension. It is important to remember that this is a medical emergency. When the cause is idiopathic hypertension, the measures consist of reducing the cerebrospinal fluid.
In this case, doctors may prescribe diuretics such as mannitol or furosemide according to Revista Chilena de Neurocirugia. In addition, weight loss can be beneficial, as well as fluid and salt restriction.
To help the cerebrospinal fluid circulate properly, it is also a good idea to lift the head end of the bed slightly. In case none of these measures work, surgery may be necessary.
The surgical approach consists of performing a lumbar puncture to empty some of the fluid. Finally, if the cause is an infection or there is an abscess due to bacterial colonization, the patient must receive antibiotics.

What you need to keep in mind about this condition
What we need to keep in mind when it comes to papillary edema is that it is a pathology that affects the optic nerve. It is produced by an increase in intracranial pressure that responds to many different situations. However, most cases have one thing in common: An increase in pressure inside the skull.
One of the most common causes is idiopathic intracranial hypertension. However, brain tumors, bleeding and infections can be a trigger. Papillary edema should be treated as a medical emergency to prevent irreparable visual impairment.